Localization for Onboarding: Global User Experiences
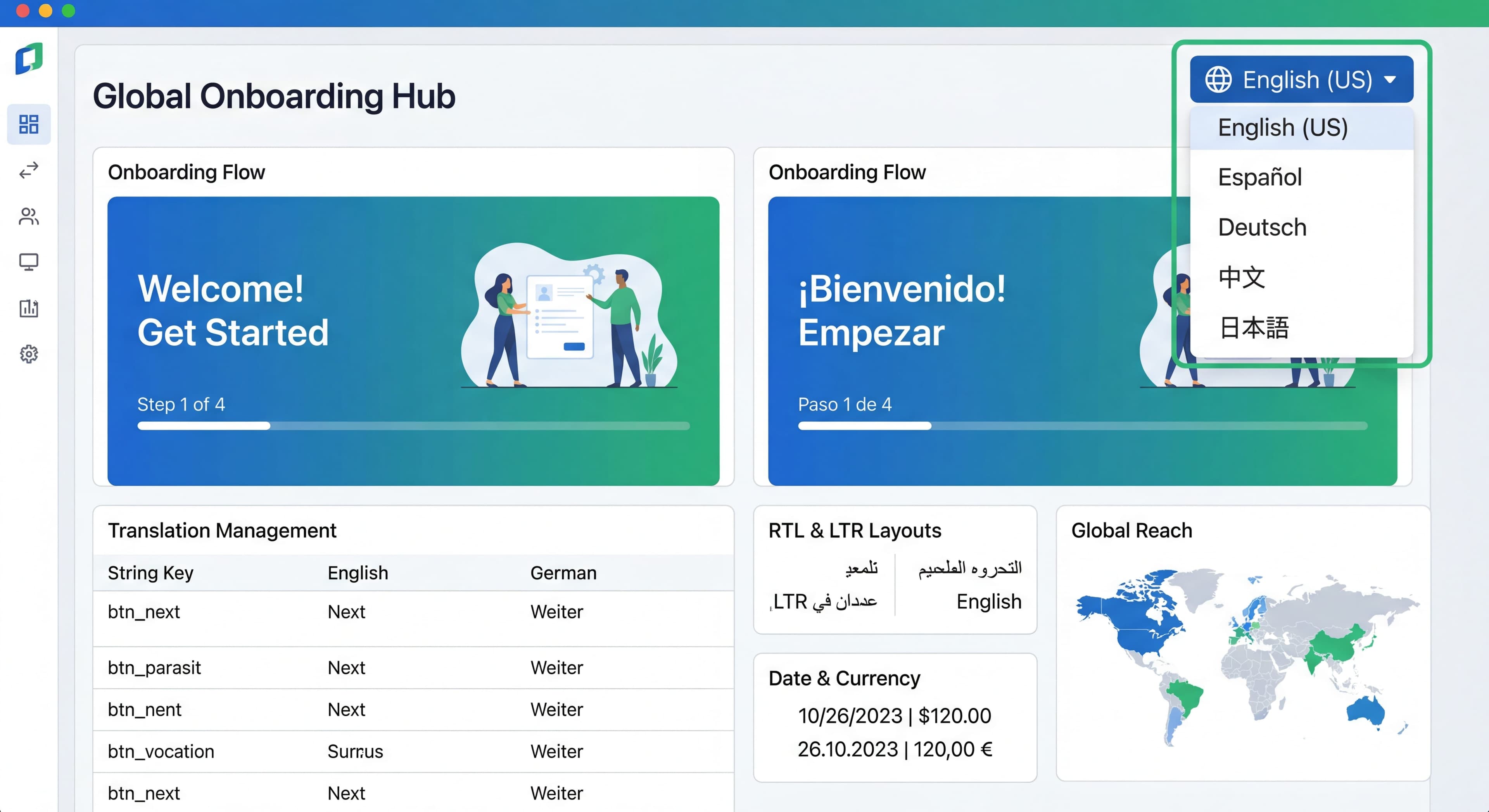
Your product serves users worldwide, but your onboarding only speaks English. That creates friction for international users and leaves growth on the table. Onboarding localization isn't just translation. It's adapting the entire experience for different languages, cultures, and expectations.
This guide covers how to localize your onboarding effectively for global users.
Onboarding only in English?
Create step-by-step guides that work across languages and help global users succeed with Glitter AI.
Why Localize Onboarding
The Business Case
Digital products can theoretically reach worldwide markets, but language barriers create invisible walls. The statistics here are pretty clear: 75% of internet users are non-native English speakers. Research shows users are 4 times more likely to purchase products that communicate in their native language. And 56% of consumers say getting information in their own language matters more than price. These aren't edge cases. They're fundamental requirements for capturing international market share.
Onboarding magnifies the importance of localization because it's users' first real interaction with your product. Marketing might attract international users with compelling promises, but onboarding has to deliver on those promises in language they fully understand. First impressions during onboarding set the tone for the entire relationship. Confusion or frustration in those first minutes often leads to permanent abandonment. Non-English speakers naturally struggle more with complex instructions and technical terminology in their second or third language. What's perfectly clear guidance for native English speakers becomes an exhausting cognitive challenge for others, directly impacting completion rates and activation.
The impact on international market performance is measurable. Companies expanding globally without localizing onboarding see predictable results: activation rates in non-English markets lag 30-50% behind English-speaking markets, early churn among international users runs higher than domestic cohorts, and support teams get flooded with basic questions in other languages. Users who don't fully understand onboarding instructions make mistakes, encounter problems, and need support intervention for issues that proper multilingual onboarding would prevent.
Impact on Metrics
Without onboarding localization, international expansion often underperforms in ways that are hard to diagnose without proper segmentation. Lower activation in non-English markets might get blamed on product-market fit or competitive dynamics when the real issue is that users can't understand how to get started. Higher early churn internationally looks like a retention problem when it's actually an onboarding comprehension problem. More support tickets in other languages becomes a staffing challenge when it's really a symptom of inadequate self-service resources. These issues compound as frustrated international users leave negative reviews, creating reputation barriers that persist long after you eventually localize.
With proper localization, the transformation can be striking. Companies consistently report 30-50% improvement in international activation rates after implementing quality localization. Support burden drops because users can self-serve through translate product tours and localized guidance. Better NPS from international users reflects the respect they feel when companies invest in speaking their language. These improvements translate directly to revenue growth as higher activation and lower churn expand international customer lifetime value.
What to Localize
Content Types
User-Facing Text:
- Welcome messages
- Product tour content
- Checklist items
- Tooltips and hotspots
- Error messages
- Email sequences
Supporting Content:
- Help documentation
- Video tutorials
- Support articles
- FAQ content
Beyond Text
Non-Text Elements:
- Images with text
- Screenshots
- Videos and voiceovers
- Icons with cultural meaning
- Date and time formats
- Number formats
- Currency displays
Localization Strategies
Strategy 1: Full Localization
What It Means:
Complete translation and adaptation of all onboarding content.
When to Use:
- Major markets with significant user base
- High-value markets worth investment
- Competitive markets where localization is expected
Investment:
High—professional translation, cultural review, ongoing maintenance.
Strategy 2: Key Language Localization
What It Means:
Localize for top 5-10 languages only.
Typical Languages:
- English (base)
- Spanish (400M+ speakers)
- Mandarin Chinese (900M+ speakers)
- French (280M+ speakers)
- German (130M+ speakers)
- Japanese (125M+ speakers)
- Portuguese (260M+ speakers)
When to Use:
- Resource constraints
- Clear language-based market priorities
- 80/20 approach to coverage
Strategy 3: Simplified Localization
What It Means:
Simplify English content to be more internationally accessible.
Tactics:
- Use plain, simple language
- Avoid idioms and cultural references
- Use international date formats
- Minimize text in images
When to Use:
- Early-stage companies
- Limited resources
- English-proficient user base
Strategy 4: Community/AI Translation
What It Means:
Use community contributions or AI translation with human review.
When to Use:
- Wide language needs, limited budget
- Non-critical content
- Iteration speed matters
Caution:
Quality varies; review before publishing.
Implementation Guide
Step 1: Internationalization (i18n)
Prepare Your Codebase:
Before translating, make content translatable.
Best Practice: Externalize Strings
// Bad: Hardcoded strings
const welcomeMessage = "Welcome to our product!";
// Good: Externalized strings
const welcomeMessage = t('onboarding.welcome.title');
String Files:
// en.json
{
"onboarding": {
"welcome": {
"title": "Welcome to our product!",
"subtitle": "Let's get you started in 3 easy steps."
},
"step1": {
"title": "Create your first project",
"description": "Projects help you organize your work."
}
}
}
Step 2: Translation
Professional Translation:
For high-quality, use professional translators who understand:
- Your product context
- Technical terminology
- Target market nuances
Translation Management:
Use platforms like:
- Lokalise
- Phrase (formerly PhraseApp)
- Crowdin
- Transifex
Process:
- Export strings from codebase
- Send to translation platform
- Translators work on content
- Review and approve translations
- Import back to codebase
Step 3: Contextual Review
Translations Need Context:
Provide translators with:
- Screenshots of where text appears
- Character limits
- Tone guidelines
- Glossary of terms
Example Context:
String: "Get started"
Context: Button on welcome modal, max 15 characters
Tone: Friendly, action-oriented
Screenshot: [attached]
Step 4: Testing
Localization Testing:
- Review in-context (actual product)
- Check text truncation
- Verify RTL languages display correctly
- Test with native speakers
Automated Checks:
- Missing translations
- Placeholder errors
- Length violations
Tool Support
DAP Localization Features
Whatfix:
- 70+ languages supported
- Built-in translation management
- Auto-translation option
Userpilot:
- Multi-language content
- Language detection
- Translation export/import
Appcues:
- Manual translation per flow
- Duplicate and translate workflow
- No auto-translation
Chameleon:
- Multi-language support
- Translation API
- Language targeting
Implementation Example
Appcues Multi-Language:
// Detect user language
const userLanguage = getUserLanguage(); // 'es', 'fr', 'de', etc.
// Configure Appcues
Appcues.identify(userId, {
language: userLanguage,
locale: userLocale
});
// Create separate flows per language
// Flow: "Welcome Tour - ES"
// Targeting: language equals "es"
Custom Implementation:
// i18n in onboarding system
const OnboardingStep = ({ step }) => {
const { t, i18n } = useTranslation();
return (
<div className="tooltip">
<h3>{t(`onboarding.${step.id}.title`)}</h3>
<p>{t(`onboarding.${step.id}.description`)}</p>
<button>{t('common.next')}</button>
</div>
);
};
Cultural Considerations
Beyond Language
Culture Affects:
- Color meanings (red = danger vs prosperity)
- Imagery expectations
- Humor appropriateness
- Formality levels
- Reading patterns
Formality Levels
Formal vs Informal:
- German: Often expects formal "Sie"
- Spanish: Varies by region (tú vs usted)
- Japanese: Multiple politeness levels
Example:
English: "You're all set!"
German (formal): "Sie sind startklar!"
German (informal): "Du bist startklar!"
Spanish (Latin America): "¡Estás listo!"
Spanish (Spain, formal): "¡Está listo!"
Date and Time
Format Differences:
US: 12/31/2025 (MM/DD/YYYY)
Europe: 31/12/2025 (DD/MM/YYYY)
ISO: 2025-12-31
12-hour: 3:30 PM
24-hour: 15:30
Implementation:
// Use locale-aware formatting
const formatDate = (date, locale) => {
return new Intl.DateTimeFormat(locale).format(date);
};
// formatDate(date, 'en-US') → "12/31/2025"
// formatDate(date, 'de-DE') → "31.12.2025"
Same questions over and over?
Create self-serve documentation that empowers users to help themselves with Glitter AI.
Numbers and Currency
Format Differences:
US: 1,234.56
Germany: 1.234,56
France: 1 234,56
Currency:
const formatCurrency = (amount, currency, locale) => {
return new Intl.NumberFormat(locale, {
style: 'currency',
currency: currency
}).format(amount);
};
// formatCurrency(1234.56, 'USD', 'en-US') → "$1,234.56"
// formatCurrency(1234.56, 'EUR', 'de-DE') → "1.234,56 €"
Right-to-Left (RTL) Languages
Languages:
Arabic, Hebrew, Farsi, Urdu
Considerations:
- Text direction reverses
- UI layout mirrors
- Icons may need flipping
CSS Implementation:
/* Base styles */
.tooltip {
text-align: left;
margin-left: 10px;
}
/* RTL override */
[dir="rtl"] .tooltip {
text-align: right;
margin-left: 0;
margin-right: 10px;
}
Content Guidelines
Writing for Translation
Do:
- Use simple, clear sentences
- Be consistent with terminology
- Leave room for text expansion
- Use complete sentences
- Provide context
Don't:
- Use idioms ("hit the ground running")
- Use culture-specific references
- Embed text in images
- Use humor that doesn't translate
- Use abbreviations
Text Expansion
Translation Length:
Text typically expands when translated:
- German: +30%
- French: +20%
- Spanish: +20%
- Japanese: -10% (but may need more height)
Design Implications:
- Button text: Allow flexible width
- Fixed containers: Test with longer text
- Character limits: Account for expansion
Glossary
Maintain Consistency:
Create a glossary of key terms:
| English | Spanish | German | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dashboard | Panel de control | Dashboard | Keep English in DE |
| Project | Proyecto | Projekt | |
| Workspace | Espacio de trabajo | Arbeitsbereich |
Same questions over and over?
Create self-serve documentation that empowers users to help themselves with Glitter AI.
Localized Images and Media
Screenshots
Options:
- Localize product, take new screenshots (best)
- Use annotation-free screenshots
- Overlay localized text on screenshots
Videos
Options:
- Re-record in each language (best quality, highest cost)
- Add localized subtitles
- Create language-neutral videos (no voiceover)
Icons
Review for Cultural Sensitivity:
- Gestures (thumbs up, OK sign vary in meaning)
- Religious symbols
- Animals (dogs problematic in some cultures)
- Color associations
Maintenance and Updates
Keeping Translations Current
Challenges:
- Content changes frequently
- New features need translation
- Old translations become stale
Process:
- Track changes to base language
- Queue changed strings for translation
- Review and approve updates
- Deploy updated translations
Version Control
Track Translation Status:
{
"onboarding.welcome.title": {
"en": "Welcome!",
"es": "¡Bienvenido!",
"de": "Willkommen!",
"fr": null, // needs translation
"lastUpdated": "2025-01-15",
"version": "2.1"
}
}
Translation Memory
Reuse Translations:
- Common phrases translate once
- Consistency across product
- Faster turnaround for updates
Measuring Localization Success
Metrics by Language
Compare:
- Activation rate by language
- Onboarding completion by language
- Time to value by language
- Support tickets by language
Example Analysis:
Language Activation Completion Support Tickets
English 42% 78% 1.2/user
Spanish 38% 71% 1.8/user
German 44% 82% 0.9/user
French 35% 65% 2.1/user
French underperformance suggests translation quality issues.
User Feedback
Survey in Native Language:
Ask localized users:
- Was onboarding clear?
- Did anything seem "off" or unnatural?
- What would improve the experience?
Common Mistakes
Mistake 1: Machine Translation Only
Problem: Unnatural, confusing text.
Fix: Human review minimum, professional translation ideal.
Mistake 2: Literal Translation
Problem: Idioms translated word-for-word.
Fix: Use professional translators who localize meaning.
Mistake 3: Forgetting Non-Text Elements
Problem: Screenshots still in English.
Fix: Localize all user-facing content.
Mistake 4: One-Time Effort
Problem: Translations become stale.
Fix: Build translation into content workflow.
Mistake 5: Ignoring Cultural Context
Problem: Content inappropriate for culture.
Fix: Include cultural review in localization process.
Translating the same guides?
Create step-by-step SOPs once and adapt them for any market with Glitter AI.
The Bottom Line
Onboarding localization transforms your onboarding from English-only to truly global. It's an investment that pays off in international growth, user satisfaction, and competitive advantage.
Key Principles:
- Start with key languages (80/20 rule)
- Build internationalization into the product from the start
- Use professional translation for critical content
- Consider cultural context, not just language
- Measure and improve by market
The goal isn't perfect translation everywhere. It's meaningful improvement for your most important international onboarding experiences.
Continue learning: First-Time User Experience and User Segmentation for Onboarding.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is localizing onboarding important for global SaaS products?
With 75% of internet users being non-native English speakers and users being 4x more likely to purchase in their native language, localized onboarding significantly impacts international growth. Companies typically see 30-50% improvement in international activation rates, reduced support burden, and better NPS from international users after localizing.
What onboarding content should I prioritize for translation?
Prioritize user-facing text first: welcome messages, product tour content, checklist items, tooltips, error messages, and email sequences. Then localize supporting content like help documentation and video tutorials. Also consider non-text elements like screenshots, date/time formats, number formats, and currency displays.
How do I translate product tours in no-code onboarding tools?
Most DAPs support multi-language content through different approaches: Whatfix supports 70+ languages with built-in translation management, Userpilot offers language detection and translation export/import, Appcues requires duplicating flows and translating manually, and Chameleon provides multi-language support with a translation API.
What cultural considerations matter beyond language translation?
Culture affects color meanings (red means danger in some cultures, prosperity in others), imagery expectations, humor appropriateness, formality levels (German formal Sie vs informal Du), and reading patterns for RTL languages. Date formats, number formats, and currency displays also vary significantly by region and need proper localization.
How do I measure if my localized onboarding is successful?
Compare activation rates, onboarding completion rates, time to value, and support tickets by language. If one language significantly underperforms others (for example, 35% activation vs 42% average), it suggests translation quality issues. Survey localized users in their native language asking if onboarding was clear and what seemed unnatural.
