Onboarding for B2B SaaS: Enterprise Considerations
B2B onboarding plays by different rules than B2C. You're not dealing with one person making one decision. There are multiple stakeholders with competing priorities, implementation timelines measured in weeks or months, and organizational politics that affect whether anyone actually uses your product. The person who signs the contract often isn't the person who has to use it every day.
This guide tackles the specific challenges of B2B onboarding and what to do about them.
Enterprise onboarding too complex?
Create step-by-step guides that simplify multi-stakeholder onboarding with Glitter AI.
B2B vs B2C Onboarding Differences
Decision vs. Usage
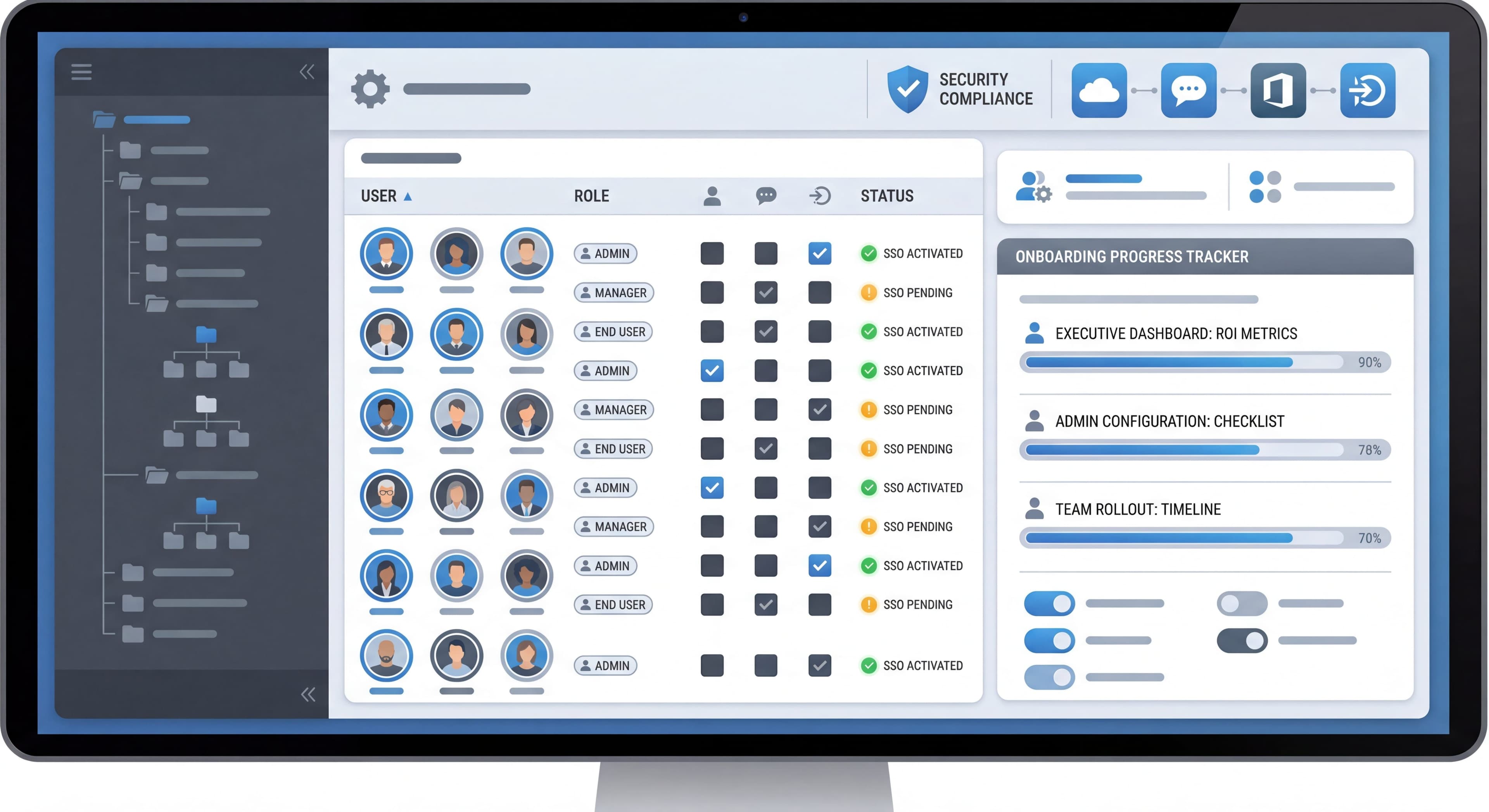
The biggest structural difference comes down to who makes decisions versus who uses the product. In B2C, it's usually the same person. Someone downloads an app, evaluates it themselves, pays their own money, and experiences the result firsthand. One persona, one journey. Simple.
B2B fragments this across multiple people with different agendas. The executive who approved the budget wants ROI metrics and strategic alignment, but they might never actually log in. The IT admin cares about security compliance and integration headaches. The team manager wants to know if this will actually make their team more productive. And the end users? They just want something that helps them do their job without learning a whole new system. According to B2B SaaS onboarding research, you have to satisfy all these different definitions of success at the same time: technical implementation for admins, productivity gains for managers, usability for the people actually clicking buttons.
Buying Cycles
B2C buying happens fast. Someone finds an app, reads a few reviews, maybe tries a free version, downloads it. The whole thing can happen in one sitting. Stakes are low, decisions are easily reversed, no approval workflows needed.
B2B buying takes weeks or months. Even mid-market purchases involve committees, vendor comparisons, security reviews, procurement negotiations, budget approvals. According to enterprise onboarding strategies, enterprise deals can take 6-12 months before anyone even logs in. By the time users show up for onboarding, they've already formed expectations. They have specific use cases in mind. There's organizational pressure to make this work because people have already committed.
Implementation Complexity
B2C onboarding is all about instant gratification. Download it, use it, get value in minutes. No documentation required. The best consumer apps work immediately with smart defaults. Customize later if you want.
B2B is inherently messier. You're integrating with existing systems like CRM, authentication, and data warehouses. Migrating data from legacy systems. Configuring workflows to match how the organization actually operates. Training different user types. Research from B2B SaaS growth strategies shows companies that nail time-to-value report 38% higher performance scores and 62% better conversion rates. But in B2B, fast time-to-value means balancing thorough setup against the desire for quick wins. Staged rollouts where you progressively configure things are increasingly common because they hit both targets.
Stakeholder Management
B2C: One person to satisfy.
B2B: Multiple stakeholders with sometimes competing priorities:
- Executive sponsor (ROI, strategy)
- IT admin (security, integration)
- Manager (team productivity)
- End user (daily utility)
- Finance (cost control)
Risk Tolerance
B2C: Low switching cost if it doesn't work.
B2B: High stakes. Failed implementations reflect on decision-makers.
Multi-Stakeholder Onboarding
Identify Key Personas
The Executive Sponsor:
- Needs: ROI visibility, strategic alignment, minimal involvement
- Onboarding: Quick value demonstration, executive summary dashboards
- Success: Product delivers promised business outcomes
The Admin/Implementer:
- Needs: Configuration control, user management, integration setup
- Onboarding: Technical documentation, setup wizards, security controls
- Success: Smooth rollout with minimal problems
The Team Manager:
- Needs: Team adoption, productivity impact, usage visibility
- Onboarding: Team setup flows, adoption tracking, workflow templates
- Success: Team uses product effectively
The End User:
- Needs: Easy learning curve, daily utility, minimal disruption
- Onboarding: Feature-specific guidance, quick reference, help access
- Success: Product makes their job easier
Designing for Multiple Personas
Role-Based Entry Points:
- Detect role during signup or first login
- Route to role-appropriate onboarding path
- Show relevant features and hide irrelevant ones
Parallel Onboarding Tracks:
- Admin track: Configuration, integration, user management
- User track: Core features, daily workflow
- Manager track: Team setup, reporting
Handoff Points:
- Admin completes setup → Invites team → Team receives user onboarding
- Clear transitions between responsibilities
Admin vs User Onboarding Paths
Admin Onboarding Focus
Admins need to configure the product for the organization:
Account Setup:
- Organization details
- Billing information
- Security settings (SSO, 2FA requirements)
- Compliance configurations
Integration Setup:
- Connect to existing tools (CRM, email, calendar)
- API configuration
- Data import/migration
- Webhook setup
User Management:
- Invite initial users
- Set up roles and permissions
- Define access controls
- Configure team structure
Workspace Configuration:
- Templates and defaults
- Branding (if applicable)
- Workflow customization
- Notification settings
User Onboarding Focus
End users need to accomplish their daily work:
Core Feature Introduction:
- Primary workflow demonstration
- Key actions for their role
- Quick reference for common tasks
Context-Specific Guidance:
- Based on their assigned role
- Based on their team's workflow
- Based on their use case
Self-Service Resources:
- Help documentation
- Video tutorials
- Community access
Timing and Sequencing
Before User Invitation:
Admin completes enough setup that users arrive to a configured workspace.
At User Invitation:
Users receive context about why they're being invited and what to expect.
First User Login:
Tailored onboarding based on what admin has configured.
Team Onboarding Strategies
The Pilot Approach
Process:
- Onboard small pilot team first
- Learn from pilot experience
- Refine approach
- Expand to broader organization
Benefits:
- Lower risk initial rollout
- Real feedback before scale
- Champion development
- Process refinement opportunity
The Champion Program
Process:
- Identify enthusiastic early adopters
- Give them advanced training
- Have them support peer onboarding
- Scale through champions
Benefits:
- Peer-to-peer learning
- Cultural adoption
- Scalable support
- Internal advocates
The Department Rollout
Process:
- Onboard one department completely
- Document what works
- Replicate for next department
- Adjust for department differences
Benefits:
- Concentrated support resources
- Complete adoption in each unit
- Manageable scope
- Learnings compound
Integration Onboarding
Many B2B products require integrations to deliver value.
Integration Discovery
During Signup:
- Ask about existing tool stack
- Prioritize relevant integrations
During Setup:
- Highlight critical integrations
- Show value of connecting
Integration Setup Flow
Make It Easy:
- OAuth where possible (no API keys)
- Clear step-by-step instructions
- Verification that connection works
- Troubleshooting guidance
Show Value Quickly:
- Immediate data sync after connect
- "Your data is flowing" confirmation
- Example of integration in action
Common Integration Challenges
Authentication Complexity:
Different organizations have different IT policies. Support multiple auth methods.
Data Mapping:
Fields don't match 1:1. Provide mapping tools or smart defaults.
Permission Requirements:
Users may not have authority to connect. Provide instructions for IT.
Sync Timing:
Clarify when data will appear and what syncs automatically vs. manually.
Success Milestones
Training taking too long?
Create step-by-step guides that get users productive faster with Glitter AI.
Define B2B Success Metrics
Implementation Milestones:
- Account configured
- Critical integrations connected
- Initial users invited
- First team workflow completed
Adoption Milestones:
- X% of invited users activated
- Y actions completed per user
- Z features adopted
Value Milestones:
- First [outcome] achieved
- Time to first value
- ROI indicators
Tracking and Communication
Internal Tracking:
- Health scores by account
- Milestone completion rates
- Risk indicators
Customer Communication:
- Progress updates to sponsors
- Adoption reports to managers
- Next step guidance
Customer Success Handoffs
The Handoff Problem
Sales closes → Customer goes silent → CS inherits without context → Customer frustrated with repetition.
Information to Transfer
From Sales to Implementation:
- Why they bought (problems to solve)
- Key stakeholders and roles
- Technical environment
- Timeline expectations
- Special agreements or promises
From Implementation to CS:
- What was configured
- Who was trained
- Current adoption status
- Outstanding issues
- Champion identification
Smooth Transition Strategies
Shared Systems:
- CRM with complete history
- Notes in customer success platform
- Recorded calls and meetings
Transition Calls:
- Introduce new point of contact
- Summarize progress
- Align on next phase
Customer-Facing Visibility:
- Give customers access to their status
- Show who their contacts are
- Provide self-service options
Training taking too long?
Create step-by-step guides that get users productive faster with Glitter AI.
Common B2B Onboarding Challenges
The Ghost Champion
Initial champion leaves company. Product usage drops.
Solution:
- Multi-thread relationships
- Document knowledge in product
- Create organizational stickiness (integrations, data)
The Pilot That Doesn't Scale
Successful pilot but organization-wide adoption fails.
Solution:
- Plan for scale from the start
- Different onboarding for broad rollout
- Executive communication strategy
The Partial Implementation
Customer set up 60% and stopped. Value unrealized.
Solution:
- Health monitoring and alerts
- Proactive outreach at stall points
- Implementation milestones with check-ins
The Integration Blocker
Can't proceed without integration that has blockers.
Solution:
- Alternative paths that deliver partial value
- IT liaison support
- Executive escalation paths
The Training Gap
Admins onboarded, users weren't.
Solution:
- User onboarding separate from admin setup
- Self-serve training resources
- Scalable user education
B2B Onboarding Timeline Example
Week 1: Kickoff
- Welcome call with stakeholders
- Account configuration
- Integration planning
Week 2-3: Technical Setup
- Integration connections
- Data migration
- Admin training
Week 4: Pilot Users
- Small group onboarded
- Feedback collection
- Workflow refinement
Week 5-6: Team Rollout
- Broader user invitation
- User onboarding resources
- Champion support
Week 7-8: Optimization
- Adoption review
- Additional training
- Advanced feature introduction
Week 9+: Steady State
- Handoff to CS
- Regular check-ins
- Expansion opportunities
Measuring B2B Onboarding Success
Account-Level Metrics
- Time to first value
- Implementation completion rate
- Integration activation rate
- Stakeholder engagement
User-Level Metrics
- User activation rate
- Feature adoption breadth
- Return session rate
- Support ticket volume
Business Metrics
- Time to ROI achievement
- Expansion within account
- Logo retention
- Account health score
Team rollouts stalling?
Create step-by-step guides that help admins and users onboard themselves with Glitter AI.
Building B2B Onboarding
- Map stakeholders and their distinct needs
- Design parallel paths for different roles
- Plan for scale from pilot to organization
- Build handoff processes that transfer context
- Measure at multiple levels (account, team, user)
- Iterate based on feedback from all stakeholders
B2B onboarding is definitely more complex than B2C. But the core principles stay the same: understand what people need, reduce friction, show value fast, and keep supporting success over time.
Continue learning: Mobile App Onboarding and Team Onboarding Strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is B2B SaaS onboarding different from B2C onboarding?
B2B onboarding involves multiple stakeholders (executives, admins, managers, end users) with different needs, longer implementation cycles, integration requirements, and higher stakes. The decision-maker, buyer, and end users are often different people.
What is the best approach for enterprise software onboarding?
Design parallel onboarding tracks for different roles - admin paths for configuration and user management, and user paths for core features and daily workflows. Use role-based entry points, clear handoff processes, and measure success at account, team, and user levels.
How do you onboard multiple stakeholders in B2B SaaS?
Identify key personas (executive sponsor, admin, team manager, end user) and design specific experiences for each. Route users to role-appropriate onboarding paths at first login, and ensure admins complete setup before inviting team members to a configured workspace.
What is a good B2B onboarding timeline?
A typical enterprise timeline spans 8+ weeks: Week 1 for kickoff and configuration, Weeks 2-3 for technical setup and integrations, Week 4 for pilot users, Weeks 5-6 for team rollout, Weeks 7-8 for optimization, then ongoing customer success support.
How do you handle customer success handoffs during B2B onboarding?
Transfer key information including why they bought, stakeholder roles, technical environment, timeline expectations, what was configured, who was trained, current adoption status, and identified champions. Use shared CRM systems, transition calls, and give customers visibility into their status.
